CF1209H.Moving Walkways
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
Airports often use moving walkways to help you walking big distances faster. Each such walkway has some speed that effectively increases your speed. You can stand on such a walkway and let it move you, or you could also walk and then your effective speed is your walking speed plus walkway's speed.
Limak wants to get from point 0 to point L on a straight line. There are n disjoint walkways in between. The i -th walkway is described by two integers xi and yi and a real value si . The i -th walkway starts at xi , ends at yi and has speed si .
Every walkway is located inside the segment [0,L] and no two walkways have positive intersection. However, they can touch by endpoints.
Limak needs to decide how to distribute his energy. For example, it might make more sense to stand somewhere (or to walk slowly) to then have a lot of energy to walk faster.
Limak's initial energy is 0 and it must never drop below that value. At any moment, he can walk with any speed v in the interval [0,2] and it will cost him v energy per second, but he continuously recovers energy with speed of 1 energy per second. So, when he walks with speed v , his energy increases by (1−v) . Note that negative value would mean losing energy.
In particular, he can walk with speed 1 and this won't change his energy at all, while walking with speed 0.77 effectively gives him 0.23 energy per second.
Limak can choose his speed arbitrarily (any real value in interval [0,2] ) at every moment of time (including the moments when he is located on non-integer positions). Everything is continuous (non-discrete).
What is the fastest time Limak can get from 0 to L ?
输入格式
The first line contains integers n and L ( 1≤n≤200000 , 1≤L≤109 ), the number of walkways and the distance to walk.
Each of the next n lines contains integers xi , yi and real value si ( 0≤xi<yi≤L , 0.1≤si≤10.0 ). The value si is given with at most 9 digits after decimal point.
It's guaranteed, that no two walkways have a positive intersection. The walkways are listed from left to right. That is, yi≤xi+1 for 1≤i≤n−1 .
输出格式
Print one real value, the fastest possible time to reach L . Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error won't exceed 10−9 .
输入输出样例
输入#1
1 5 0 2 2.0
输出#1
3.000000000000
输入#2
1 5 2 4 0.91
输出#2
3.808900523560
输入#3
3 1000 0 990 1.777777 995 996 1.123456789 996 1000 2.0
输出#3
361.568848429553
说明/提示
The drawings show the first two examples. In the first one, there is a walkway from 0 to 2 with speed 2.0 and Limak wants to get to point 5 . The second example has a walkway from 2 to 4 with speed 0.91 .
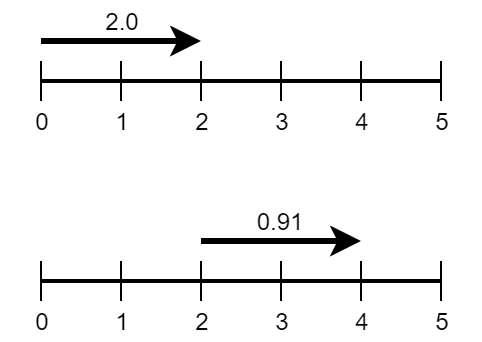 In the first example, one of optimal strategies is as follows.
In the first example, one of optimal strategies is as follows.
- Get from 0 to 2 by standing still on the walkway. It moves you with speed 2 so it takes 1 second and you save up 1 energy.
- Get from 2 to 4 by walking with max speed 2 for next 1 second. It takes 1 second again and the energy drops to 0 .
- Get from 4 to 5 by walking with speed 1 . It takes 1 second and the energy stays constant at the value 0 .
The total time is 1+1+1=3 .